Bhai, Big O Notation samajhna ekdum zaruri hai agar tumhe DSA (Data Structures and Algorithms) mein master banna hai. Ye algorithm ki performance aur efficiency ko samajhne ka ek standard tareeka hai. Chal basic aur examples ke saath samajhte hain:
What is Big O Notation?
- Big O Notation ek ==mathematical concept hai jo algorithm ke time complexity aur space complexity ko analyze karta hai.==
- Ye batata hai ki input size (n) ke badhne par algorithm ka performance kaise change hoga.
Why is Big O Important?
- Predict Performance: Ye help karta hai kisi algorithm ka behavior predict karne mein jab input size kaafi bada ho.
- Compare Algorithms: Algorithms ke efficiency compare karne ke liye use hota hai.
- Optimization: Code ko fast aur memory-efficient banane ke liye.
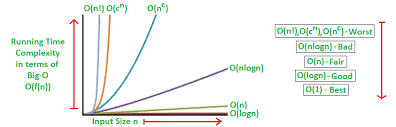
Common Big O Notations
| Big O | Name | Example | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|
| O(1) | Constant Time | Accessing an array element | Best (Fastest) |
| O(log n) | Logarithmic Time | Binary Search | Very Fast |
| O(n) | Linear Time | Iterating through an array | Moderate |
| O(n log n) | Log-Linear Time | Merge Sort, Quick Sort (Best/Average) | Moderate |
| O(n²) | Quadratic Time | Nested loops (e.g., Bubble Sort) | Slow |
| O(2^n) | Exponential Time | Recursive Fibonacci | Very Slow |
| O(n!) | Factorial Time | Solving Traveling Salesman | Worst (Slowest) |
Time Complexity Examples
-
O(1) - Constant Time
- Independent of input size.
int getFirstElement(int[] arr) { return arr[0]; // Sirf ek step } -
O(log n) - Logarithmic Time
- Input size half hota jata hai har step par (e.g., Binary Search).
int binarySearch(int[] arr, int target) { int low = 0, high = arr.length - 1; while (low <= high) { int mid = low + (high - low) / 2; if (arr[mid] == target) return mid; else if (arr[mid] < target) low = mid + 1; else high = mid - 1; } return -1; } -
O(n) - Linear Time
- Ek loop jo input ke size ke proportional chale.
int findMax(int[] arr) { int max = arr[0]; for (int num : arr) { if (num > max) max = num; } return max; } -
O(n²) - Quadratic Time
- Nested loops ke case mein.
void printPairs(int[] arr) { for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) { System.out.println(arr[i] + ", " + arr[j]); } } } -
O(2^n) - Exponential Time
- Recursive solutions jisme choices kaafi hoti hain (e.g., Fibonacci).
int fibonacci(int n) { if (n <= 1) return n; return fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2); }
Space Complexity
- Space complexity algorithm ke memory usage ko represent karta hai.
- Example:
- Iterative algorithms usually O(1) hoti hain (constant memory).
- Recursive algorithms stack space use karte hain.
Key Points to Remember
- Focus on Growth Rate: Big O input size ke growth pe zyada focus karta hai, exact runtime par nahi.
- Dominant Term Consider Karo: Sirf sabse bada term count hota hai.
- Example:
O(n² + n)⇒ Dominant termO(n²)hoga.
- Example:
- Best, Worst, Average Cases:
- Best case: Algorithm ka sabse fast scenario.
- Worst case: Sabse slow scenario (important for Big O).
- Average case: Typical performance.
Comparison Example
| Algorithm | Input Size n=10n = 10 | Input Size n=100n = 100 |
|---|---|---|
| O(1) | 1 | 1 |
| O(log n) | ~3 | ~7 |
| O(n) | 10 | 100 |
| O(n log n) | ~30 | ~700 |
| O(n²) | 100 | 10,000 |
| O(2^n) | 1,024 | Too large |
Bhai, agar kisi specific algorithm ya example pe Big O ko samajhna ho, toh bol. Har complexity ko real-world mein relatable bana ke samjha dunga! 😎