HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is the standard language used to create web pages. It structures the content on the web, such as headings, paragraphs, images, links, and more.\
Basic HTML Syntax
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My First Page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello, World!</h1>
<p>This is my first HTML page.</p>
</body>
</html>Key Components:
<!DOCTYPE html>: Declares the document type.<html>: The root of the HTML document.<head>: Contains metadata like the title of the page.<body>: Contains all the visible content of the page.









The anchor element


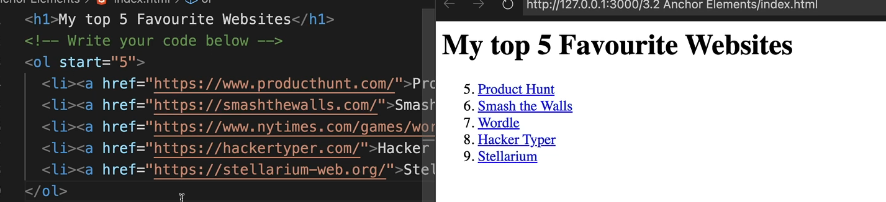
Image element
<img src = "url" />

List of majority tags used in html website
Here’s a table with HTML tags and their explanations for easy reference:
| Tag | Description |
|---|---|
<!DOCTYPE html> | Declares the document type (HTML5). |
<html> | Root element of the HTML document. |
<head> | Contains metadata, styles, and scripts. |
<title> | Sets the title of the page (visible in the browser tab). |
<meta> | Defines metadata like character encoding, description, and keywords. |
<link> | Links external resources like stylesheets. |
<style> | Embeds CSS styles directly in the document. |
<script> | Embeds or links JavaScript. |
<body> | Contains the visible content of the page. |
<h1> - <h6> | Headings from largest (<h1>) to smallest (<h6>). |
<p> | Defines a paragraph. |
<br> | Inserts a line break. |
<hr> | Inserts a horizontal rule (divider line). |
<strong> | Makes text bold with semantic emphasis. |
<b> | Makes text bold without semantic meaning. |
<em> | Makes text italic with semantic emphasis. |
<i> | Makes text italic without semantic meaning. |
<u> | Underlines text. |
<mark> | Highlights text. |
<small> | Reduces font size. |
<del> | Represents deleted (strikethrough) text. |
<ins> | Represents inserted (underlined) text. |
<sup> | Displays text as superscript. |
<sub> | Displays text as subscript. |
<a> | Creates a hyperlink. |
<img> | Embeds an image. |
<audio> | Embeds audio content. |
<video> | Embeds video content. |
<source> | Specifies multiple media sources for <audio> or <video>. |
<track> | Adds subtitles or captions to <video> or <audio>. |
<ul> | Creates an unordered (bulleted) list. |
<ol> | Creates an ordered (numbered) list. |
<li> | Represents a list item. |
<dl> | Creates a definition list. |
<dt> | Represents a term in a definition list. |
<dd> | Represents the description/definition of a term. |
<table> | Creates a table. |
<tr> | Defines a table row. |
<td> | Defines a table cell. |
<th> | Defines a table header cell. |
<caption> | Adds a caption to a table. |
<col> | Specifies column properties in a table. |
<colgroup> | Groups multiple <col> elements. |
<form> | Defines a form for collecting user input. |
<input> | Accepts user input (text, radio, checkbox, etc.). |
<textarea> | Creates a multi-line text input field. |
<button> | Creates a clickable button. |
<label> | Labels a form element for accessibility. |
<fieldset> | Groups related elements in a form. |
<legend> | Provides a title for a <fieldset>. |
<select> | Creates a dropdown menu. |
<option> | Represents an item in a dropdown list. |
<datalist> | Defines a list of predefined options for an input field. |
<optgroup> | Groups related options in a dropdown list. |
<header> | Defines the header of a page or section. |
<footer> | Defines the footer of a page or section. |
<section> | Defines a section of content. |
<article> | Defines independent, self-contained content. |
<nav> | Defines navigation links. |
<aside> | Defines content related to the main content (e.g., a sidebar). |
<main> | Specifies the main content of a document. |
<div> | Creates a block-level container for grouping elements. |
<span> | Creates an inline container for styling or grouping text. |
<iframe> | Embeds another webpage within the current page. |
<canvas> | Used for drawing graphics via JavaScript. |
<svg> | Embeds scalable vector graphics (SVG). |
<map> & <area> | Define clickable regions in an image (image map). |
<progress> | Displays progress of a task (e.g., a loading bar). |
<meter> | Represents a value within a specific range (e.g., temperature, scores). |
<template> | Defines reusable HTML fragments. |
<details> | Creates a collapsible section of content. |
<summary> | Provides a summary for a collapsible <details> element. |
<noscript> | Displays alternative content if JavaScript is disabled. |
code for html site where we used majority of tags
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>HTML Tags Demo</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css">
</head>
<body>
<header>
<h1>HTML Tags Demonstration</h1>
<p>Learn the major HTML tags with examples and usage</p>
</header>
<section>
<h2>1. Basic Document Structure</h2>
<p>The basic structure of an HTML document includes the following tags:</p>
<div class="example">
<pre>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Document Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Page Content Goes Here -->
</body>
</html>
</pre>
</div>
<h2>2. Headings</h2>
<p>Headings are used to structure the content. There are six levels from <code><h1></code> to <code><h6></code>:</p>
<div class="example">
<h1>Heading 1</h1>
<h2>Heading 2</h2>
<h3>Heading 3</h3>
<h4>Heading 4</h4>
<h5>Heading 5</h5>
<h6>Heading 6</h6>
</div>
<h2>3. Paragraphs and Line Breaks</h2>
<p>The <code><p></code> tag defines a paragraph. Use <code><br></code> for line breaks:</p>
<div class="example">
<p>This is a paragraph. It has some text to demonstrate how it looks.</p>
<p>This is another paragraph with a <br> line break in it.</p>
</div>
<h2>4. Links</h2>
<p>The <code><a></code> tag creates hyperlinks:</p>
<div class="example">
<a href="https://www.google.com" target="_blank">Visit Google</a>
</div>
<h2>5. Images</h2>
<p>The <code><img></code> tag embeds an image:</p>
<div class="example">
<img src="https://via.placeholder.com/150" alt="Placeholder Image">
</div>
<h2>6. Lists</h2>
<p>HTML supports ordered (<code><ol></code>) and unordered (<code><ul></code>) lists:</p>
<div class="example">
<h3>Unordered List</h3>
<ul>
<li>Item 1</li>
<li>Item 2</li>
<li>Item 3</li>
</ul>
<h3>Ordered List</h3>
<ol>
<li>First Item</li>
<li>Second Item</li>
<li>Third Item</li>
</ol>
</div>
<h2>7. Tables</h2>
<p>The <code><table></code> tag creates a table. Use <code><tr></code> for rows, <code><td></code> for cells, and <code><th></code> for headers:</p>
<div class="example">
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Age</th>
<th>City</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>John</td>
<td>25</td>
<td>New York</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Jane</td>
<td>30</td>
<td>London</td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
<h2>8. Forms</h2>
<p>The <code><form></code> tag collects user input:</p>
<div class="example">
<form>
<label for="name">Name:</label>
<input type="text" id="name" name="name">
<br><br>
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email">
<br><br>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
</div>
<h2>9. Semantic Tags</h2>
<p>Semantic tags like <code><header></code>, <code><footer></code>, <code><article></code>, and <code><section></code> make content meaningful:</p>
<div class="example">
<header>Header Section</header>
<article>
<h3>Article Title</h3>
<p>This is an article.</p>
</article>
<footer>Footer Section</footer>
</div>
</section>
<footer>
<p>HTML Tags Demo Website | Created for Learning</p>
</footer>
</body>
</html>
code for styles.css
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
line-height: 1.6;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
header {
background: #007BFF;
color: white;
padding: 10px 20px;
text-align: center;
}
section {
margin: 20px auto;
max-width: 900px;
}
.example {
background: #f4f4f4;
padding: 10px;
margin: 10px 0;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 5px;
}
.example pre {
background: #ddd;
padding: 10px;
overflow: auto;
border-radius: 5px;
}
footer {
background: #333;
color: white;
text-align: center;
padding: 10px 0;
position: relative;
bottom: 0;
width: 100%;
}