Python Conditions and If statements
Python supports the usual logical conditions from mathematics:
- Equals: a == b
- Not Equals: a != b
- Less than: a < b
- Less than or equal to: a ⇐ b
- Greater than: a > b
- Greater than or equal to: a >= b
An “if statement” is written by using the if keyword.
a = 33
b = 55
if b > a:
print("b is greater than a")
# b is greater than a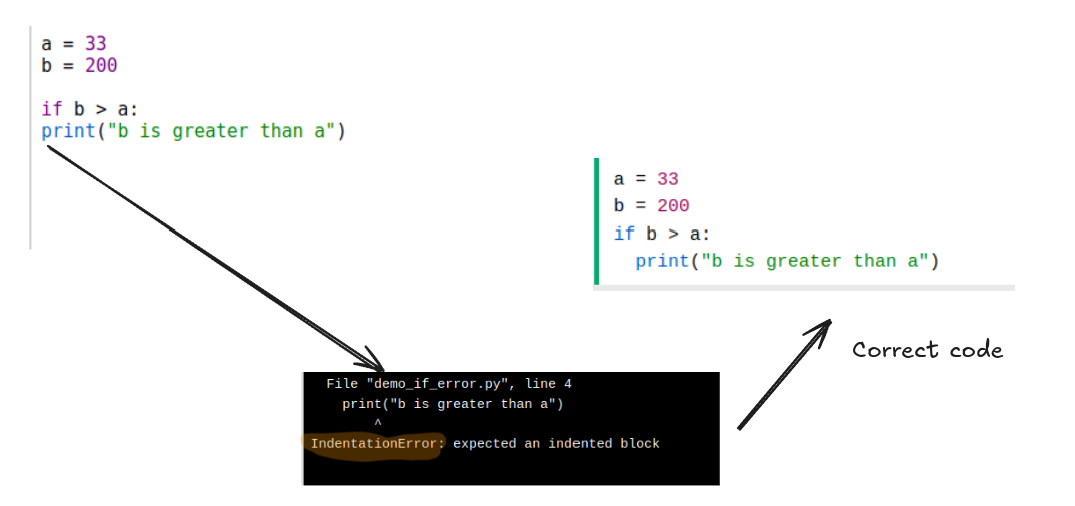
Elif
The elif keyword is Python’s way of saying “if the previous conditions were not true, then try this condition”.
a = 33
b = 33
if b > a:
print("b is greater than a")
elif a == b:
print("b equal to a")
# a and b are equalElse
The else keyword catches anything which isn’t caught by the preceding conditions.
a = 200
b = 33
if b > a:
print("b is greater than a")
elif a == b:
print("a and b are equal")
else:
print("a is greater than b")
# a is greater than b Short hand if
if a > b : print("a is greater than b")Short hand if else
a = 2
b = 330
print("A") if a > b else print("B")a = 330
b = 330
print("A") if a > b else print("=") if a == b else print("B")