GitHub Actions is a continuous integration and continuous delivery/deployment (CI/CD) platform that automates your software development workflows
allows you to build, test, and deploy software source code directly from your GitHub repository by creating custom workflows or pipelines.
With various configuration options for triggers based on commits and merges
uses yaml files executed when triggered by events like code pushes, pull requests, and releases.
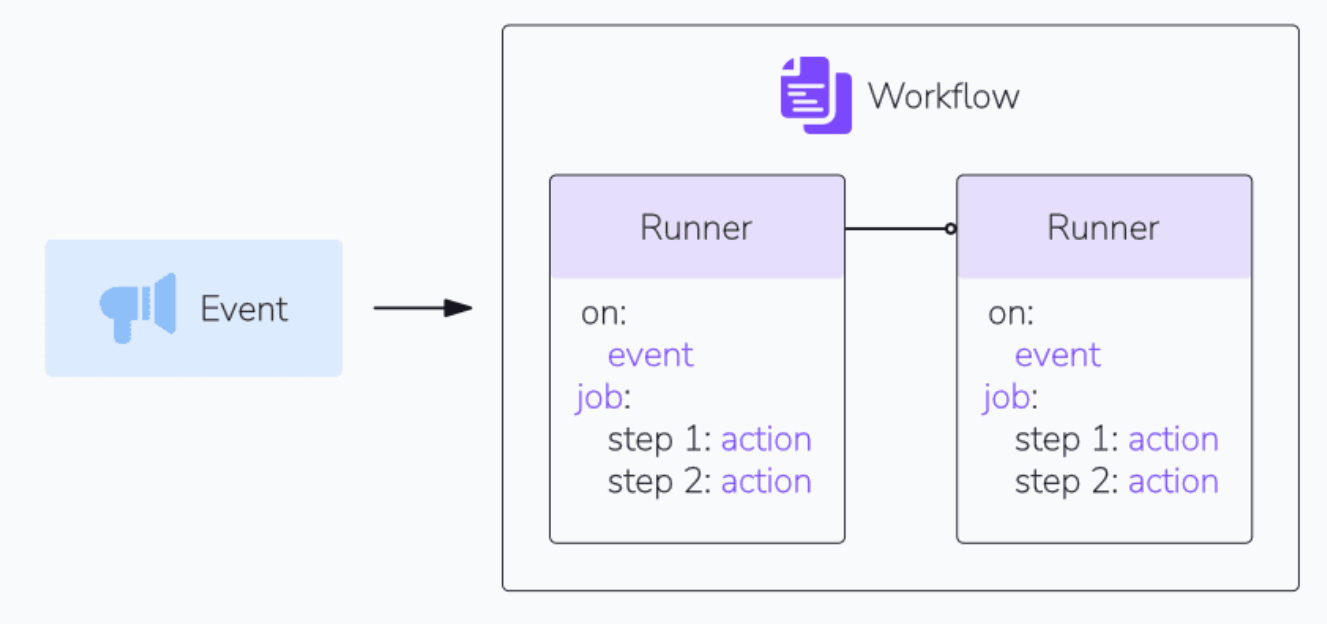
- GitHub Actions, a workflow is an automated process defined by a YAML file
- usually placed in the .github/workflows directory of any repository
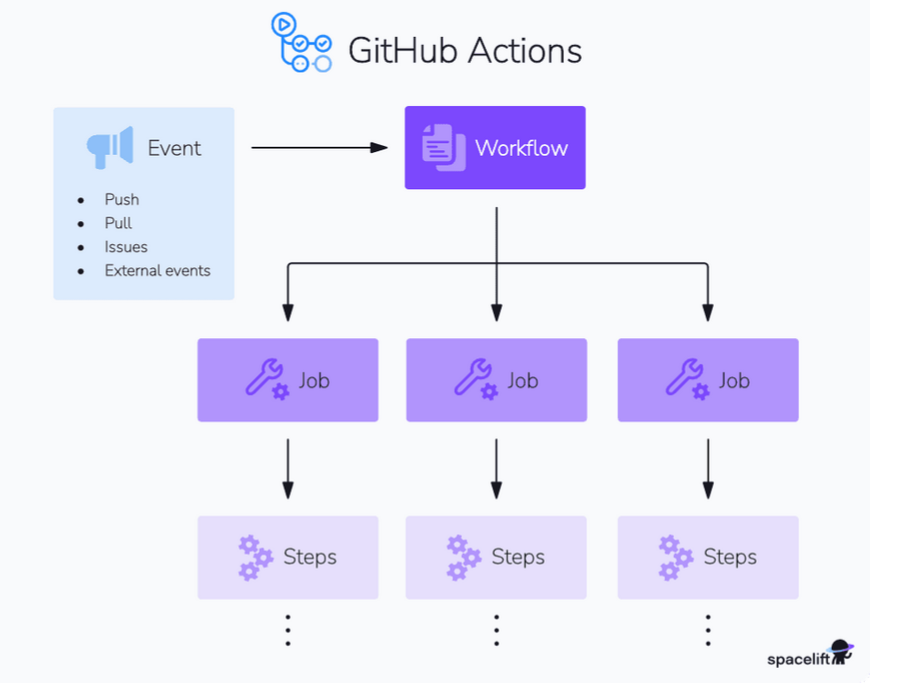
GitHub Actions events
- events are specific activities that trigger a workflow run
- trigger point for workflows , helps automate , build and deploy process
- common event of the workflow is push pull_request , schedule and workflow_dispach
- Additionally, you can fine-tune these triggers by specifying further details such as branch names, commit messages, and more.
GitHub Actions runners
Runners in GitHub Actions are virtual machines that execute jobs in a workflow
GitHub Actions jobs
GA consist of a series of series of steps executed on the same runner.
job can run either parallely or sequentially, depending on the dependencies defined in workflow
What is the difference between a GitHub action and a workflow?
A GitHub “Action” and “Workflow” are both key components of the GitHub Actions platform. A workflow is an automated process triggered by specific events like push, pull, or schedule, defined in YAML files in the .github/workflows directory. It consists of one or more jobs, each containing steps. Actions are reusable units of code within these workflows, performing individual tasks.
While workflows orchestrate automation, actions provide the building blocks, enabling task reuse across different workflows. Custom actions can be created or used from the GitHub Marketplace, facilitating efficient and consistent task execution in software development processes.
Key Concepts:
-
Workflows: Automated processes defined in YAML files within the
.github/workflowsdirectory of a repository. They are triggered by specific events. -
Events: Activities within a repository that initiate a workflow, such as pushes, pull request creation, issue updates, or scheduled times.
-
Jobs: Individual tasks within a workflow that run in parallel or sequentially. Each job executes on a designated runner.
-
Runners: Virtual machines (GitHub-hosted or self-hosted) that execute the jobs within a workflow. They can be provisioned for various operating systems like Ubuntu, Windows, and macOS.
-
Steps: A sequence of commands or actions executed within a job on a runner. Steps can include cloning the repository, installing dependencies, running tests, or deploying code.
-
Actions: Reusable units of code that perform specific tasks within a step, often found in the GitHub Marketplace or created as custom actions.
Functionality:
GitHub Actions can automate various aspects of the software development lifecycle, including:
- CI/CD: Building, testing, and deploying code automatically upon specified events.
- Code Quality and Security: Running linters, static analysis tools, and security scans.
- Repository Automation: Managing issues and pull requests, automating release processes, and handling dependency updates.
- Deployment: Deploying applications to various cloud providers or on-premises environments