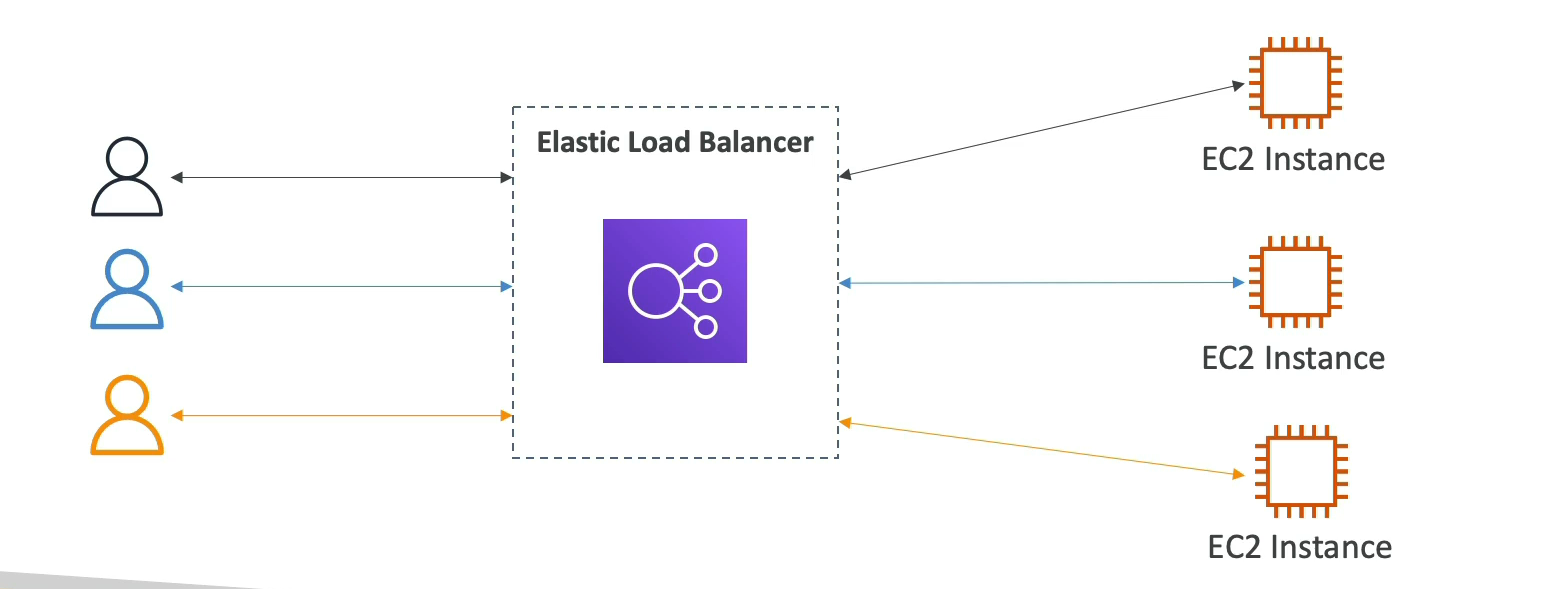
load balance are servers that forward traffic to multiple servers (eg EC2 instances) downstream
Why use LB


Cross-Zone Load Balancing
- Definition:
Cross-zone load balancing allows traffic to be evenly distributed across all Availability Zones (AZs) in a region, not just within one zone. - How it works:
- Normally, a load balancer in one AZ routes traffic only to instances in that same AZ.
- With cross-zone enabled, it can route traffic to instances in other AZs as well.
- Benefit:
- Ensures better utilization of all healthy instances, even if one AZ has fewer.
- Improves fault tolerance and load distribution
- Example:
- If you have 2 AZs
- AZ1 has 2 instances, AZ2 has 4.
- Without cross-zone → 50% traffic goes to each AZ.
- With cross-zone → traffic is balanced across all 6 instances evenly.
- If you have 2 AZs
- Cost impact:
- Some AWS load balancers (like NLB) charge for inter-AZ data transfer, so enabling it may slightly increase costs.
- Supported by:
- ALB (Application Load Balancer): Enabled by default and free.
- NLB (Network Load Balancer): Optional and can incur data transfer costs.
Connection draining in AWS
